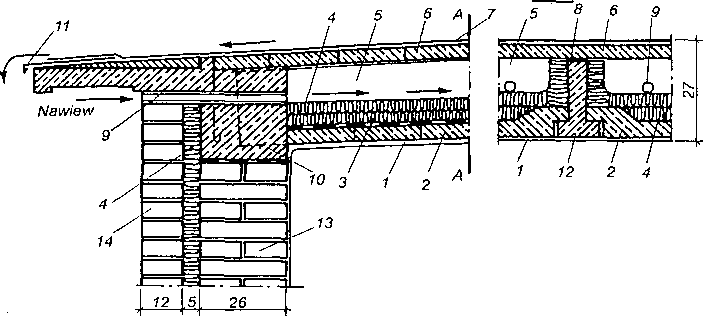
 Przykład stropodachu wentylowanego (strop T-27); 1 — tynk, 2 — płyta żelbetowa dolna, 3 — izolacja paroszczelna, 4 — ocieplenie, 5 — szczelina powietrzna, 6 — płyta żelbetowa górna, 7 — pokrycie z dwóch lub trzech warstw papy, 8 — pasek płyty pilśniowej półtwardej, 9- dren, 10 — wieniec żelbetowy, 11 — blacha, 12 — belka T-27, 13 — cegła ceramiczna, 14 — cegła silikatowa lub ceramiczna.
Przykład stropodachu wentylowanego (strop T-27); 1 — tynk, 2 — płyta żelbetowa dolna, 3 — izolacja paroszczelna, 4 — ocieplenie, 5 — szczelina powietrzna, 6 — płyta żelbetowa górna, 7 — pokrycie z dwóch lub trzech warstw papy, 8 — pasek płyty pilśniowej półtwardej, 9- dren, 10 — wieniec żelbetowy, 11 — blacha, 12 — belka T-27, 13 — cegła ceramiczna, 14 — cegła silikatowa lub ceramiczna.
Stropodachy wentylowane dwudzielne.
Na rysunku pokazano konstrukcję stropodachu wentylowanego dwudzielnego. Stropodach dwudzielny składa się ze stropu oraz dachu o nachyleniu połaci dachowej przystosowanej do rodzaju pokrycia (papa, płyty faliste itp.). W tego rodzaju stropodachach przestrzeń poddasza jest nieużytkowana, niekiedy mogą to być poddasza przełazowe.
Stropodachy dwudzielne wykonywane są o pojedynczej lub podwójnej konstrukcji nośnej. W stropodachach o pojedynczej konstrukcji ustrój nośny stanowi jeden z opisanych stropów, natomiast konstrukcja dachu przenoszona jest przez strop. Najczęściej na stropie ustawiane są ścianki ażurowe z cegły lub pustaków, na których ułożone są płyty korytkowe. Stropodachy o podwójnej konstrukcji składają się ze stropu oraz dachu.
W obu rodzajach stropodachów izolacja cieplna jest ułożona na paroizolacji ułożonej na stropie, przestrzeń powietrzna między stropem i dachem połączona jest otworami wylotowymi z otoczeniem zewnętrznym, a izolacja przeciwwodna jest ułożona na płytach dachowych. Powierzchnia przekroju poprzecznego otworów wlotowych i wylotowych powinna wynosić co najmniej 5% powierzchni stropodachu. Otwory te powinny być rozmieszczone równomiernie, aby zapewnić dobrą wymianę powietrza. Należy je osłonić siatką.
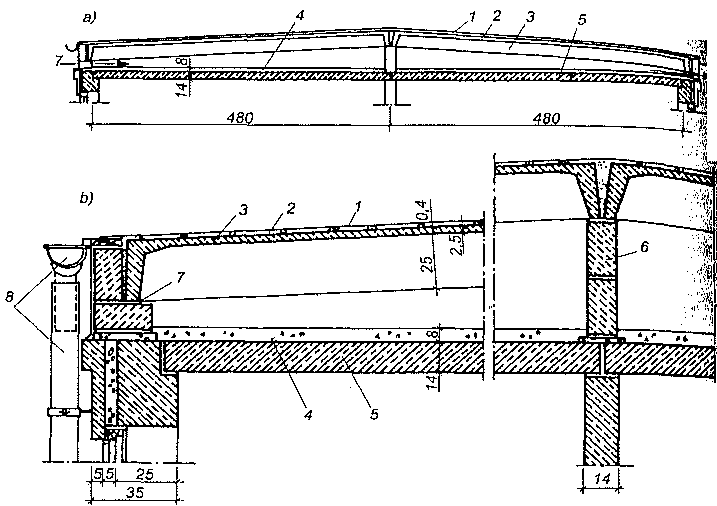 Stropodach o podwójnej konstrukcji nośnej: a) przekrój, b) szczegół konstrukcyjny 1 — dwie warstwy papy, 2 — gładź cementowa, 3 — płyta żebrowa, 4 — ocieplenie, 5 — płyta, żelbetowa, 6 — ścianka ażurowa prefabrykowana lub murowana, 7 — otwór wentylacyjny, 8 — rynna i rura spustowa.
Stropodach o podwójnej konstrukcji nośnej: a) przekrój, b) szczegół konstrukcyjny 1 — dwie warstwy papy, 2 — gładź cementowa, 3 — płyta żebrowa, 4 — ocieplenie, 5 — płyta, żelbetowa, 6 — ścianka ażurowa prefabrykowana lub murowana, 7 — otwór wentylacyjny, 8 — rynna i rura spustowa.